Table of Contents
- What is medical oxygen?
- How is oxygen supplied in healthcare?
- Medical oxygen generator – PSA plants
- Advantages and disadvantages for medical oxygen generators
- Advantages and disadvantages for bulk oxygen supply
- OXYMAT’s PSA oxygen generators – oxygen solutions for healthcare
- Conclusion
Medical oxygen generators, particularly the Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) type, are increasingly becoming vital in healthcare for their cost-effectiveness and efficiency. This post discusses their important role in medical treatments, compares them with other oxygen supply methods, and emphasizes the benefits of PSA medical oxygen generators in meeting the growing demands of healthcare.
In healthcare settings, particularly in hospitals, medical oxygen serves as a critical lifeline. High-purity oxygen is essential for a range of treatments, including respiratory therapy, anesthesia, and life support. Among the methods of oxygen supply, medical oxygen generators, especially the Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) oxygen generators, have emerged as indispensable technologies. In today’s healthcare settings, oxygen is primarily supplied through three main methods: PSA oxygen generators, oxygen concentrators, and through bulk oxygen delivery. Historically, hospitals and healthcare facilities, especially in upper-middle- and high-income economies, have depended on the practice of storing and transporting oxygen, or the method known as bulk oxygen delivery. These methods have often proved inadequate in meeting the increasing healthcare demands, a fact that became particularly evident during the COVID-19 pandemic. In contrast, low- and middle-income economies frequently struggle with the challenges of limited infrastructure and unreliable supply chains.
Furthermore, it has become evident that oxygen concentrators, as one the most widespread solution in low- and middle-income economies, are the least effective solution, particularly for critical patients. For example, one unit produces oxygen for one patient which often fall into disrepair due to the cost and complexities of maintaining them (Ref. PATH and WHO).

Oxygen delivery systems like PSA oxygen gas generators, on the other hand have become more pronounced, as they deliver stable on continuous and high purity level supply of oxygen. Unlike industrial oxygen, medical oxygen is specifically purified and produced to meet strict medical-grade standards. Weighing the distinct requirements and constraints of healthcare settings, the following sections details the three primary methods of oxygen supply, their advantages, and disadvantages.
What is medical oxygen?
Medical oxygen refers to the breathable air that is highly concentrated with oxygen molecules. It is an important component in treatments and procedures where the body’s oxygen level needs to be increased, such as supporting patients with respiratory conditions. Unlike industrial oxygen, like oxygen used in gold mining, medical oxygen is subjected to strict quality control measures to ensure a high level of purity.
How is oxygen supplied in healthcare?
As contemporarily stands, there are three main ways of oxygen supply, which include PSA oxygen generators, oxygen concentrators, and bulk oxygen delivery. Each method offers their unique advantages and disadvantages. PSA oxygen generators provide high volume and onsite oxygen production, oxygen concentrators offer portability, while bulk oxygen delivery is ideal for high-demand settings. These methods form the backbone of oxygen supply in global healthcare.
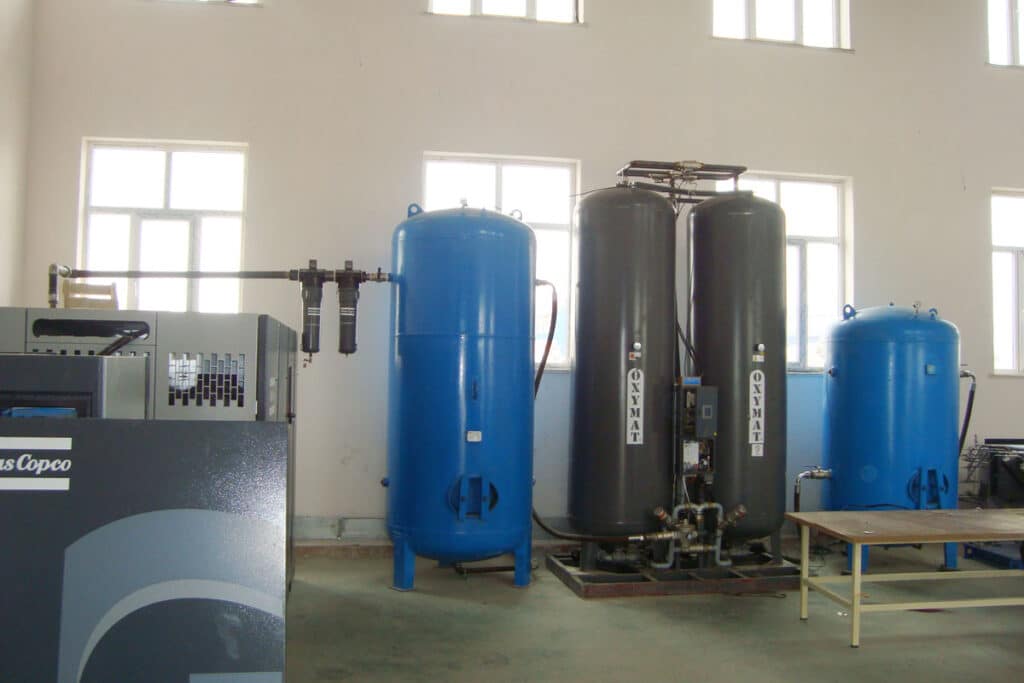
Medical oxygen generator – PSA plants
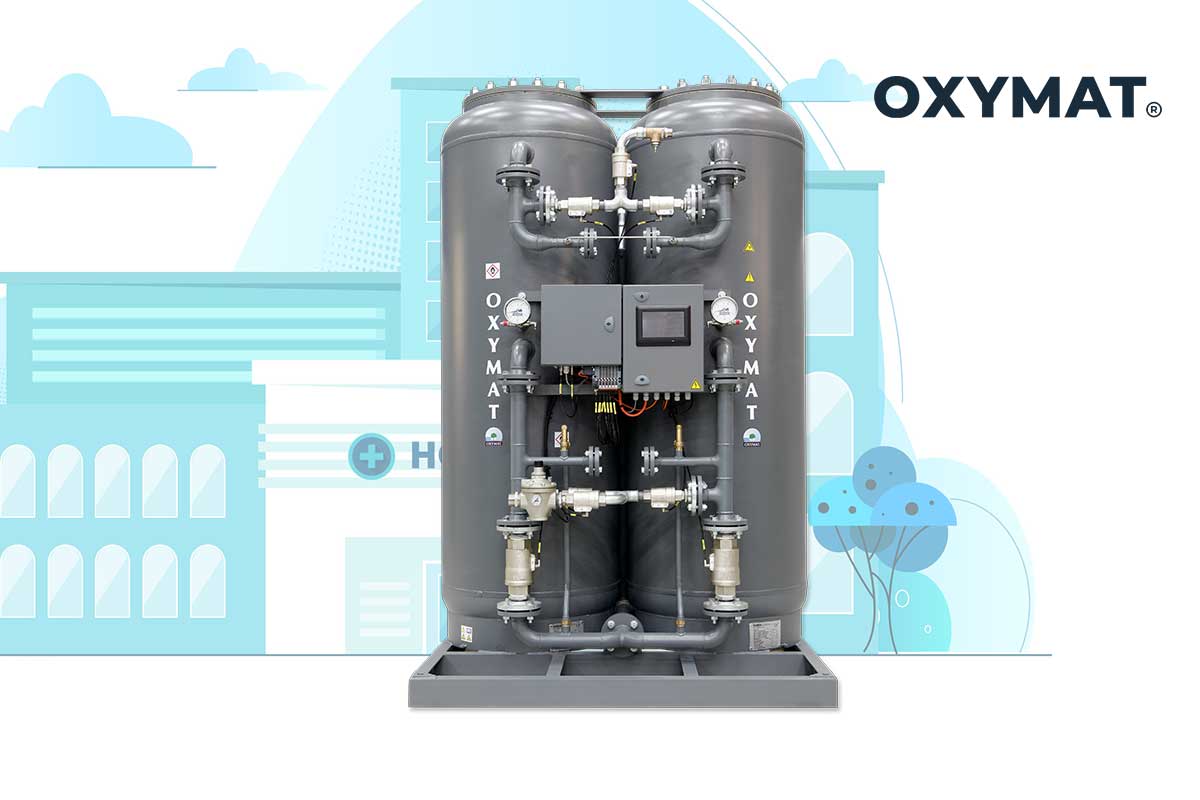
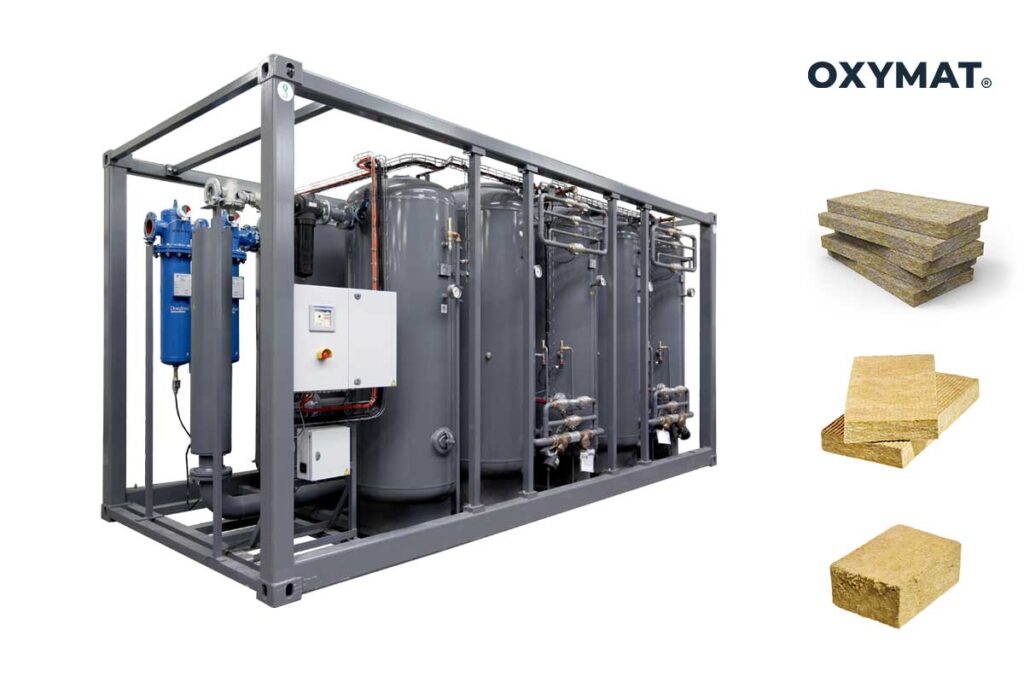
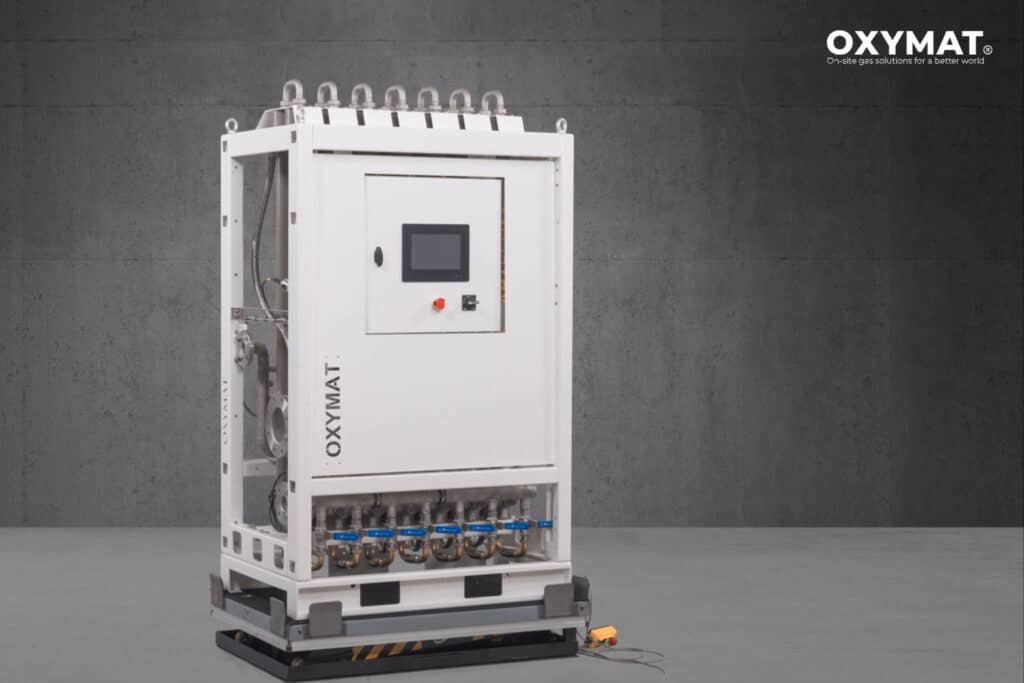
PSA oxygen plants for medical usePSA oxygen generators, also known as PSA plants, are standalone oxygen generation systems designed to produce oxygen for multiple patients simultaneously. They work by using a flow and compression process to extract oxygen from the air. PSA plants are commonly utilized in larger healthcare facilities and hospitals. While they require a significant upfront capital investment, they offer scalability and are cost-effective in delivering a consistent oxygen supply.

Small OXYMAT PSA Oxygen plant.
Advantages and disadvantages for medical oxygen generators
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Stable and continuous supply | Higher initial capital investment |
| Efficient for high oxygen demand | Energy and infrastructure requirements |
| Cost-efficient over time | Maintenance (trained personnel) |
| Reduced dependence on suppliers | |
| No need for cylinder handling | |
| Lower ongoing oxygen costs | |
| Reduced transportation risks | |
| Physical footprint | |
| Customizable oxygen concentrations | |
| Transportation (no transportation) | |
| Filling cylinders and tanks if needed |
Oxygen concentrators
Oxygen concentrators are simple devices used to extract oxygen from ambient air. They operate by removing nitrogen from the air, resulting in a concentrated oxygen supply that can be delivered to patients through nasal cannulas or masks. This method is often preferred in healthcare facilities with limited resources, particularly in low- and middle-income economies. However, apart from being advantageous in some healthcare settings, they have their noticeable limitations. As such they are only used for non-critical patients, they have short life span and have a limited oxygen purity rate, among others.
Bulk oxygen supply
Bulk oxygen supply and its storages involve the production of highly purified liquid oxygen through a process known as cryogenic fractional distillation. Liquid oxygen is stored in bulk tanks and can be distributed in various forms, such as converting it into gas and storing it in cylinders and distributing it through hospital pipelines.
Advantages and disadvantages for bulk oxygen supply
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Stable and continuous supply of oxygen | Higher initial capital investment |
| Suitable for larger healthcare facilities | Requires well-established operational model |
| Efficient for high oxygen demand | Steady demand needed for cost-effectiveness |
| Can be used in high-income countries | Requires reliable transportation infrastructure |
| Requires specialized storage and handling | |
| Complex installation | |
| Large physical footprint | |
| Safety considerations (high flammability) | |
| Cost of cryogenic infrastructure | |
| Environmental impact (transport and maintenance) | |
| Risk of supply disruptions | |
| Oxygen price fluctuations | |
| Gasification (Safety risks) |
The three methods highlighted above indicate that oxygen supply in healthcare settings faces significant challenges, and as sector does not seem to adequately be prepared for future developments. Before selecting the appropriate oxygen supply method, it is necessary to thoroughly understand the whole ecosystem. This includes addressing the increasing demands due to a growing and aging population, as well as the needs of remote or under-resourced areas.
In this context, an onsite medical oxygen generator, stand out as a most viable solution for long-term and critical needs. Their capability to deliver a stable and continuous onsite oxygen makes them fundamental in building a sustainable healthcare. As in bulk delivery, they are efficient for both high and low oxygen demand. Their dependence on a stable electricity supply, on the other hand, can pose difficulties, especially in regions with unstable electric power resources. However, incorporating renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power into their settings, can offer a solution to power-related challenges.
Additionally, what makes a PSA oxygen generator a more suitable choice, especially for hospitals and healthcare facilities that depend on oxygen bulk delivery and cylinders, is the fact that they can also be used to store the generated oxygen in cylinders and tanks. They can easily be incorporate them into already existing oxygen distribution infrastructure.
OXYMAT’s PSA oxygen generators – oxygen solutions for healthcare
OXYMAT’s PSA oxygen generators stand out for their ability to deliver stable and continuous onsite supply of oxygen. OXYMAT Two-column, known also as the Two-tower medical oxygen generator is known for their quality and reliability. Their robust build up has made them the preferred choice for many healthcare facilities and diverse healthcare environments in more than 150 countries. Depending on the healthcare facility’s settings, needs, and location, OXYMAT offers solutions either as standalone onsite oxygen generators or as turnkey solutions, equipped with service offerings.
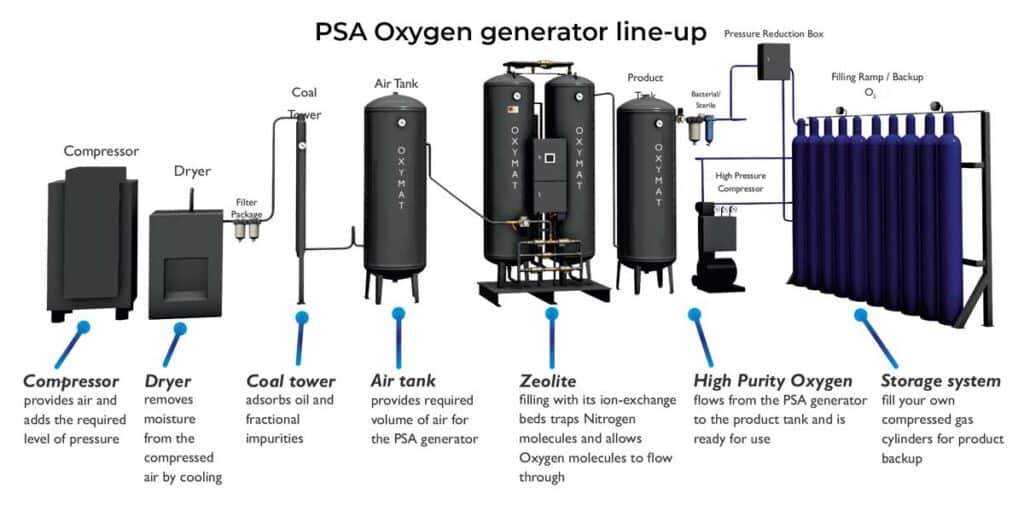
OXYMAT PSA systems consist of several components including a compressed air system, which encompasses an air compressor, refrigeration dryer, air receiver, and filters. Additionally, the turnkey solution includes a PSA skid, an oxygen receiver, and optionally, an oxygen booster and filling station, as well as a container or a frame-built solution if required. The capacity of the generators ranges from 2 to 189 Nm³/h, with purities reaching up to 95%.
Furthermore, key features of the OXYMAT oxygen generators include low energy consumption as low as 1.0 kW/m³ of oxygen, and low CO2 emissions. OXYMAT PSA oxygen generators are certified with various international approvals, including ISO 9001, ISO 13485(en), ISO 14001, and several others, ensuring compliance with global standards in healthcare and environmental management.
Conclusion
Oxygen is critical in healthcare, with PSA oxygen generators, oxygen concentrators, and bulk oxygen delivery being the primary supply methods. Each method has its pros and cons, however PSA oxygen generators emerge as a highly effective solution. They offer stable, continuous onsite oxygen production, suitable for a wide range of healthcare settings. Despite a higher initial cost and infrastructure needs, they are cost-effective in the long run, as they reduce dependency on external suppliers and are unaffected by oxygen price fluctuations. One challenge that comes with installing a PSA oxygen plant, particularly in the remote areas, is the requirement for stable electric power. However, incorporating renewable sources of energy in their settings can also eliminate these challenges.
Oxygen concentrators are more suited for non-critical patients and those in resource-limited settings. While they are simple to use, their limitations in flow, maintenance and oxygen purity, rates, maintenance etc. makes them less viable as a solution.
Bulk oxygen supply, on the other hand, is ideal for high-demand environments, yet the solution presents its own set of challenges, including transportation infrastructure, high initial investment risks and a significant environmental footprint.
OXYMAT’s PSA generators stand out with their low energy consumption, adherence to international standards, and global application, making them a preferred choice in many modern healthcare facilities for both high and low oxygen demands.



















